C++ 提供的選擇結構和 Pascal 的相似。
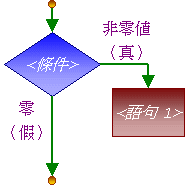 單向選擇
單向選擇 | C++ 控制結構 | 等同的 Pascal 控制結構 |
| if (<條件>) <語句1>; |
if <條件> then <語句1> |
如果 <condition> 的值不是零(即是「真」)的話,<statement_1> 將會被執行。留意在 C++ 中,then 是不需要的,但包圍著條件的括號是必須的。
如果當條件是真的時候,要有多於一個語句要執行的話,<語句1> 可以是一個複合語句。這對於所有控制結構均適用。
一個複合語句是數個被一對大括號 {} 包著的語句。右邊的大括號後面不要有分號。
程序範例︰
| C++ 版本 | Pascal 版本 |
| #include <iostream.h> main() { int OT_hours, wages = 8000; cout << "Number of overtime hours? "; cin >> OT_hours; if (OT_hours > 30) { cout << "Maximum OT hours is 30" << endl; OT_hours = 30; } wages += OT_hours * 50; cout << "Wages: $" << wages << endl; return 0; } |
program prog_11(input, output); var OT_hours, wages: integer; begin wages := 8000; write('Number of overtime hours? '); readln(OT_hours); if OT_hours > 30 then begin writeln('Maximum OT hours is 30'); OT_hours := 30 end; wages := wages + OT_hours * 50; writeln('Wages: $', wages); end. |
| 輸出範例一(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Number of overtime hours? 50 Maximum OT hours is 30 Wages: $9500 |
|
| 輸出範例二(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Number of overtime hours? 12 Wages: $8600 |
|
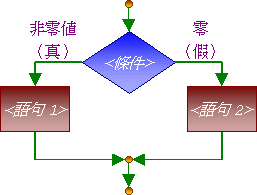 雙向選擇
雙向選擇 | C++ 控制結構 | 等同的 Pascal 控制結構 |
| if (<條件>) <語句1>; else <語句2>; |
if <條件> then <語句1> else <語句2> |
如果 <條件> 的值不是零(即是「真」),<語句1> 會被執行。否則,<語句2> 會被執行。
一個用了條件運算符的語句可以使用這個選擇結構去取代。例如,程序九可以改成以下樣子︰
| C++ 版本 | Pascal 版本 |
| #include <iostream.h> main() { int x, y, min; cout << "Enter x: "; cin >> x; cout << "Enter y: "; cin >> y; if (x < y) min = x; else min = y; cout << x; if (x > y) cout << " > "; else cout << " <= "; cout << y << endl; cout << min << " is the smaller number." << endl; return 0; } |
program prog_12(input, output); var x, y, min: integer; begin write('Enter x: '); readln(x); write('Enter y: '); readln(y); if x < y then min := x else min := y; write(x); if x > y then write(' > ') else write(' <= '); writeln(y); writeln(min, ' is the smaller number.') end. |
| 輸出範例一(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Enter x: 10 Enter y: 5 10 > 5 5 is the smaller number. |
|
| 輸出範例二(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Enter x: 4 Enter y: 7 4 <= 7 4 is the smaller number. |
|
如 Pascal 一般,C++ 也支援嵌套的控制結構。
當有幾個情況要我們選擇時,我們可以使用嵌套的 if-else 語句。例如,以下程序跟據輸入的分數輸出一個等級名稱。縮排的格式展示了那些 if-else 語句是如何被嵌套的。
| C++ 版本 | Pascal 版本 |
| #include <iostream.h> main() { int score; char grade; cout << "Score? "; cin >> score; if (score >= 80) grade = 'A'; else // score < 80 if (score >= 70) grade = 'B'; else // score < 70 if (score >= 60) grade = 'C'; else // score < 60 if (score >= 50) grade = 'D'; else // score < 50 grade = 'F'; cout << "Grade: " << grade << endl; return 0; } |
program prog_13; var score: integer; grade: char; begin write('Score? '); readln(score); if score >= 80 then grade := 'A' else (* score < 80 *) if score >= 70 then grade := 'B' else (* score < 70 *) if score >= 60 then grade := 'C' else (* score < 60 *) if score >= 50 then grade := 'D' else (* score < 50 *) grade := 'F'; writeln('Grade: ', grade) end. |
| 輸出範例一(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Score? 74 Grade: B |
|
| 輸出範例二(紅色的文字由使用者輸入)︰ | |
| Score? 32 Grade: F |
|
但為了增加可讀性,嵌套的 if-else
語句通常都會寫成以下的樣子︰
if (score >=80)
grade = 'A';
else if (score >= 70)
grade = 'B';
else if (score >= 60)
grade = 'C';
else if (score >= 50)
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';